Search results: 1295

136202_Bauko Central School_Science_Grade 5_Quarter 4_Module 1_How Rocks Turn into Soil
This module is a product of the Curriculum Implementation Division particularly the Learning Resource Management and Development Unit, Department of Education, Schools Division of Mountain Province which is in response to the implementation of the K to 12 Curriculum.
This learning Material is a property of the Department of Education- CID, Schools Division of Mountain Province. It aims to improve students’ performance specifically in Science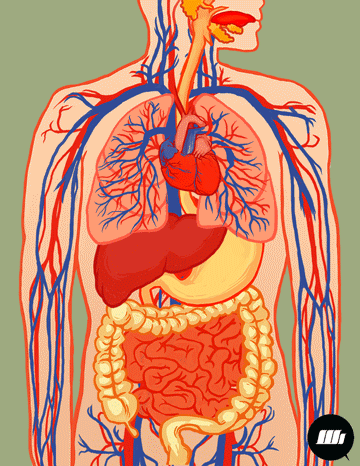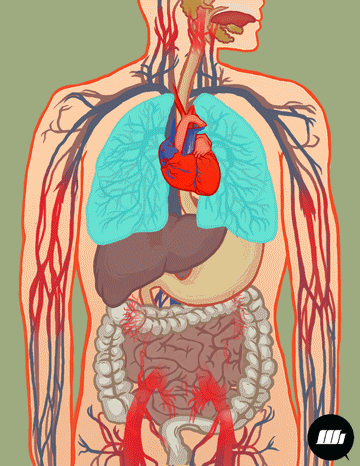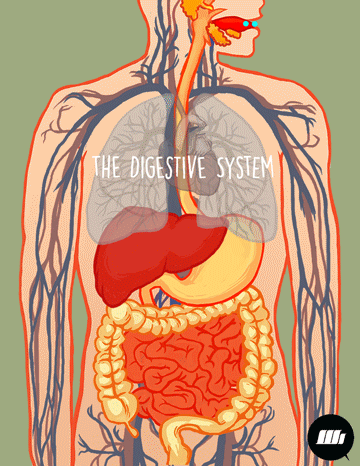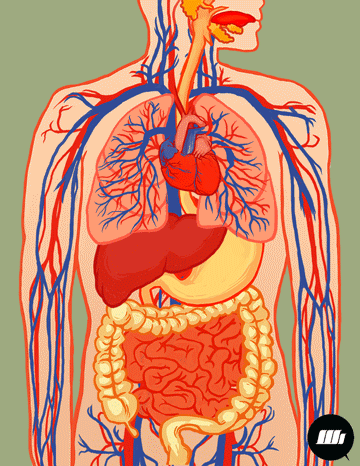
221501_Kias Elementary School_Science_Grade 4_Second Quarter_Major Body Organs Working Together
This module is in response to the implementation of the K to 12 Curriculum. This Learning Material aims to improve students’ performance specifically in Science.
302446-Alimodian National Comprehensive High School-Statistics and Probability-Grade 11-Quarter 3-Module 1-Random Variable
As previously learned in Junior High School lessons, there are lots of wonders in nature or in real-life, like tossing a coin or rolling a die, whose outcomes cannot be predicted with certainty in advance, but the set of all the possible outcomes is known. These are what we call as random phenomena or random experiments.
A random experiment is a mechanism that produces a definite outcome that cannot be predicted with certainty. The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space. The sample space associated with a random experiment is the set of all possible outcomes. An event is a subset of the sample space.
Remember that a variable is a characteristic or attribute that can assume different values. We use capital letters to denote or represent a variable. A variable X whose value depends on the outcome of a random process is called a random variable. A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon. It is a capacity that connects a real number with every component in the sample space. It is a variable whose qualities are controlled by chance. In this manner, a random variable is a numerical amount that is derived from the results of an arbitrary trial or experiment.
A random variable can be discrete or continuous.
Discrete Random Variables are variables that can take on a finite number of distinct values.
Continuous Random Variables are random variables that take an interminably uncountable number of potential values, regularly measurable amounts.
302446-Alimodian National Comprehensive high School-Statistics and Probability-Grade 11-Quarter 3-Module 2:Discrete and Continuous Random Variable
A random variable’s possible values might represent the possible outcomes of a yet-to-be-performed experiment, or the possible outcomes of a past experiment whose already-existing value is uncertain (for example, as a result of incomplete information or imprecise measurements). They may also conceptually represent either the results of an “objectively” random process (such as rolling a die), or the “subjective” randomness that results from incomplete knowledge of a quantity.
Random variables can be classified as either discrete (that is, taking any of a specified list of exact values) or as continuous (taking any numerical value in an interval or collection of intervals). In probability and statistics, the mathematical function describing the possible values of a random variable and their associated probabilities is known as a probability distribution.
Discrete random variables are variables whose values are obtained by counting. These are variables that can take on a finite number of distinct values.
For example, you can count the number of the students in a section. You can count the Covid-19 patients in a hospital.
Continuous random variables are variables whose value are obtained by measuring. These are random variables that take an interminably uncountable number of potential values, regularly measurable amounts.
302446-Alimodian National Comprehensive High School-Statistics and Probability-Grade 11-Quarter 3-Module 3:Values of a Random Variable
A random variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. We use a capital letter, like X, Y, or Z to avoid confusion with the variables used in Algebra or we can use any letter in the alphabet.
A random variable has a probability distribution (will be discussed in the next activity sheet) that represents the likelihood that any of the possible values would occur. Let’s take for example that the random variable, X, is the number on the top face of a die when it is rolled once. The possible values for X will be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Another classic example of a random variable is the outcome of tossing a coin. We consider a probability distribution in which the outcomes of a random event are not equally likely to happen. If random variable, Z, is the number of tails we get from tossing three coins, then Z could be 0, 1, 2 or 3. This means that we could have no tails, one tail, two tails or three tails on a three-coin toss.

305-107-Grade 10- Lovelace Cassiopeia- ENGLISH
English is known to be one of the most important languages in the world. There are many reasons why English is so important for us to learn. One of the reasons is that English is spoken as the second language in our country thus the need to educate ourselves with this language.

305107- Grade 10- Lovalace- MAPEH
MAPEH is a group of subjects in school. It stands for Music, Art, Physical Education, and Health. They are important because they culturally enrich students and help them enjoy and learn new things. Motor skills are also important.

305107- Grade 10- Lovelace- Filipino
Ang
Modyul 5 ay tatalakay sa isang
Nobela mula sa Cuba. Bagaman ito’y isinulat ng isang Amerikano, may
napakahalagang gampanin naman ang lugar kung saan ito naisulat dahil sesentro
ito sa pamumuhay, paniniwala at tradisyon ng mga taga-Cuba. Ang bansang Cuba ay
matatagpuan sa Hilagang bahagi ng Caribbean kung saan nagkakasalubong ang Dagat
Caribbean, Gulpo ng Mexico at Karagatang Atlantic. Binubuo ito ng mga isla at
kapuluang pinalilibutan ng Mexico (Yucatan Peninsula) sa Kanluran, Estado ng
Florida, USA at Bahamas sa Hilaga, Haiti sa Silangan at Jamaica at Cayman
Islands sa Timog.




